The Importance of Mould Temperature Control in Manufacturing
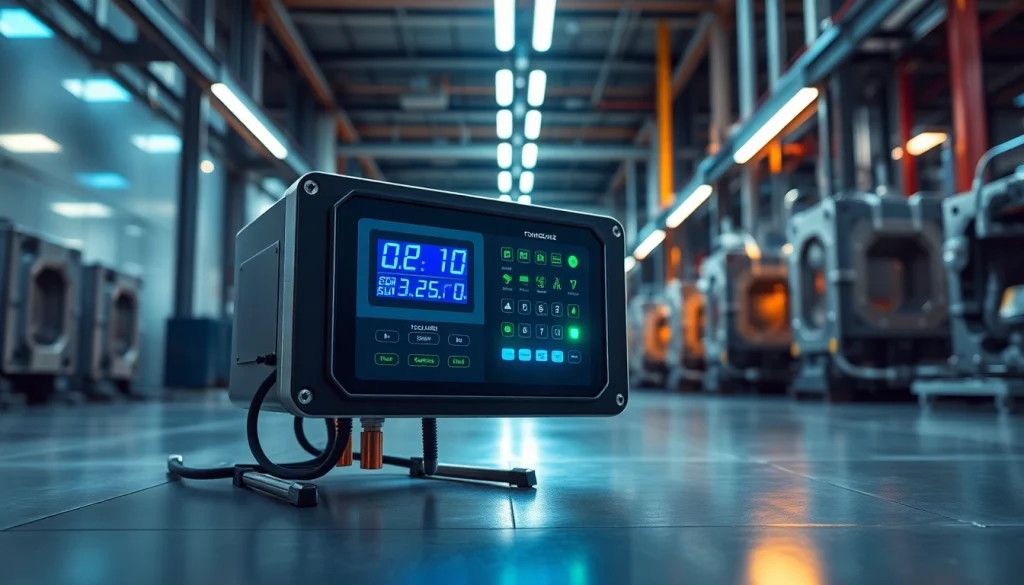
In the fast-paced world of industrial manufacturing, achieving optimal product quality while maximizing efficiency is paramount. One critical component that plays an essential role in this process is the Mould Temperature Controller. This device helps regulate and stabilize the temperature of molds during production, which in turn affects the properties of the molded products. By maintaining precise temperature control, manufacturers can significantly reduce defects, enhance yield, and streamline their production processes. As advancements continue to shape the industry, understanding how these controllers operate becomes vital for staying competitive.
When exploring options, Mould Temperature Controller solutions from industry leaders like Topstar are becoming increasingly sophisticated, accommodating various needs across different manufacturing sectors.
What is a Mould Temperature Controller?
A Mould Temperature Controller is a device used to regulate the temperature of molds in various manufacturing processes, particularly in plastic injection molding. The controller maintains the desired temperature range, ensuring that the material solidifies properly and maintains its desired properties. This device can be integrated into existing manufacturing lines and is designed for ease of use, energy efficiency, and high accuracy.
Key Benefits for Industrial Applications
- Improved Product Quality: Consistent temperature control minimizes defects such as warping or dimensional inaccuracies, leading to higher quality products.
- Increased Production Efficiency: By reducing wait times and mold changeover times through advanced cooling technologies, manufacturers can ramp up production rates.
- Energy Savings: Efficient thermal management can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption across the production process.
- Longer Mold Life: By preventing thermal shock and excessive wear, temperature controllers extend the life of molds and reduce maintenance costs.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Overall improvements in efficiency and product quality contribute to lower costs, enhancing profitability.
Challenges in Traditional Temperature Control Methods
Traditional methods of temperature control often rely on water or oil heating systems, which can be slow and inefficient. These methods may struggle to provide the rapid cooling and heating necessary for today’s fast-paced manufacturing environments. Additionally, fluctuations in temperature can lead to inconsistencies in product quality and increased scrap rates. Consequently, many businesses are turning to advanced solutions like the fourth-generation mould temperature controllers to overcome these challenges.
Understanding the Fourth-Generation Technology
The fourth-generation mould temperature controller represents a significant evolution in temperature management technology. Unlike older models, this new generation incorporates innovative features that enhance control, accuracy, and efficiency.
Advanced Features of Mould Temperature Controller
Modern mould temperature controllers are equipped with features such as:
- Forced Cooling: This allows for rapid cooling of molds, significantly reducing downtime during mold changeovers.
- Timed Power On/Off: This function enables preheating and cooling schedules, optimizing production processes further.
- PID Control Algorithm: This advanced algorithm ensures high accuracy temperature management, leading to uniform heat distribution.
PID Control Algorithm: Enhancing Accuracy
The Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control algorithm is a key component of modern mould temperature controllers. This algorithm continuously calculates the error value as the difference between a desired setpoint and a measured process variable. By adjusting the controller output, it reduces the error over time, allowing for temperature control accuracies of ±0.1℃. This precision is crucial for maintaining consistent product quality and improving overall production efficiency.
Impact of Solid-State Relays on Response Time
Solid-state relays (SSRs) also enhance the performance of mould temperature controllers. Unlike traditional mechanical relays, SSRs offer faster response times, often less than 0.1 seconds. This rapid response capability allows for real-time adjustments to temperature fluctuations, ensuring that the mold remains within optimal thermal thresholds.
Installation and Operational Guidelines
To fully leverage the capabilities of a mould temperature controller, proper installation and operational practices are crucial.
Best Practices for Setting Up the Controller
- Location: Install the controller in a dry, accessible location to facilitate maintenance and operation.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the system to ensure it maintains accurate readings.
- Integration: Ensure that the controller is properly integrated with existing systems and workflows for optimal performance.
Common Operational Challenges and Solutions
While modern mould temperature controllers mitigate many challenges, operators may still encounter issues such as:
- Inconsistent Temperatures: Regular maintenance and calibration can help to address fluctuations.
- System Failures: Implementing redundancies and regular inspections can prevent unexpected downtime.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity and Performance
Routine maintenance is fundamental to the longevity of mould temperature controllers. This includes:
- Checking and replacing filters to ensure proper water flow.
- Inspecting electrical connections to prevent failures.
- Cleaning components to avoid scaling and buildup that may affect performance.
Case Studies: Mould Temperature Control in Action
Examining real-world applications of mould temperature controllers can provide valuable insights into their effectiveness.
Success Stories from the Manufacturing Sector
Many manufacturers have reported substantial benefits after integrating advanced mould temperature controllers into their processes. For example, a leading automotive parts manufacturer increased its production efficiency by approximately 20% after implementing a fourth-generation controller, significantly reducing mold change times.
Before and After: Efficiency Metrics
In another case, a plastics manufacturer transitioned from traditional cooling systems to a modern temperature controller, resulting in:
- A 30% reduction in energy consumption
- A decrease in product defects from 5% to less than 1%
- Shortened production cycles, allowing for faster time-to-market
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
These case studies highlight the importance of investing in modern temperature control solutions. Key takeaways include the need for continuous monitoring of temperature settings and the importance of employee training to ensure optimal usage of the technology.
Future Trends in Mould Temperature Control
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of mould temperature control. Staying ahead of these trends is essential for manufacturers looking to improve their processes.
Innovations on the Horizon for 2025
In 2025, we can expect further advancements in temperature controller technology, including increased integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities. These innovations will allow for smarter and more efficient temperature management systems.
The Role of AI and IoT in Temperature Management
AI-driven analytics will enable predictive maintenance, where systems can forecast failures before they occur, allowing manufacturers to schedule downtime proactively. IoT integration will facilitate real-time monitoring and reporting, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven decisions that optimize production.
Predicting Changes in Industry Standards and Regulations
As sustainability and efficiency become paramount, regulatory frameworks surrounding energy consumption and emissions will likely tighten. Manufacturers must stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance and to leverage technologies that meet or exceed new standards.