The Significance of the Pyramids of Giza
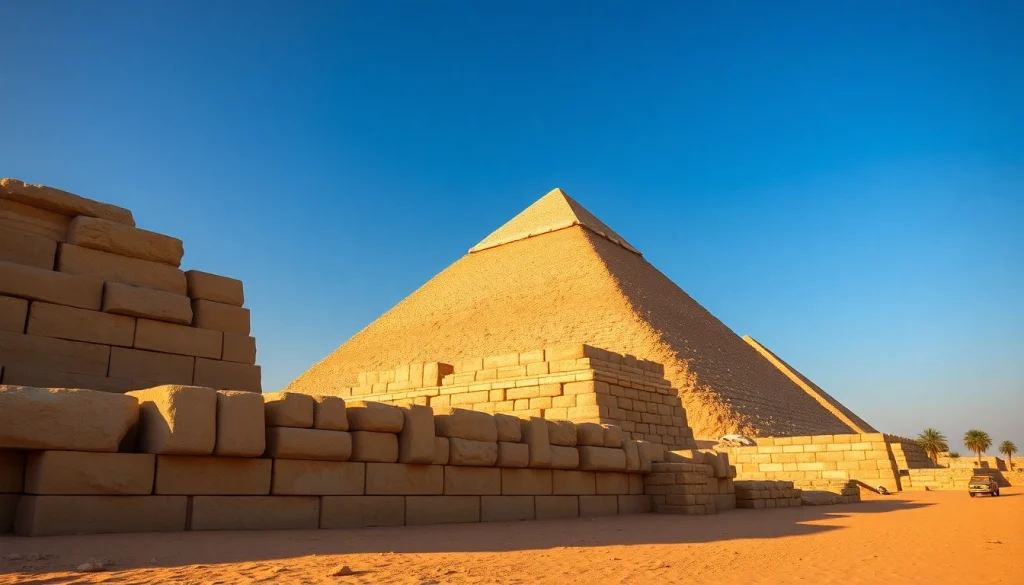
The Pyramids of Giza stand as enduring symbols of ancient Egyptian civilization, showcasing remarkable engineering and monumental artistry. They were primarily constructed as elaborate tombs for pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. The pyramids reflect the socio-political and religious priorities of the ancient Egyptians, echoing their beliefs about the afterlife and the divine. More than mere grave markers, they are testaments to the extraordinary capabilities of ancient Egyptian society. For those interested in diving deeper into this intriguing topic, https://piraminds.com/ offers a wealth of information.
Historical Context and Timeline
The Pyramids of Giza, including the Great Pyramid of Khufu (Cheops), the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure, were constructed on the Giza Plateau, near Cairo. They represent the culmination of pyramid construction techniques that began during the Third Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. The timeline of their construction reveals a staggering ambitious project that spanned several decades, with the Great Pyramid’s construction estimated to have taken about 20 years. This era signifies a critical juncture in Egypt’s history, where powerful pharaohs centralized authority and resource allocation towards monumental projects.
Architectural Marvels and Innovations
The architectural innovations present in the Pyramids of Giza still amaze scholars and engineers today. The Great Pyramid, originally standing at 146.6 meters, utilized over 2 million limestone blocks, meticulously cut and arranged to create its iconic shape. Innovations included the development of the corbel arch, which allowed for the weight of the stones to be distributed evenly. Additionally, the alignment of the pyramids with astrological precision displays an advanced understanding of astronomy among the builders, further adding to their significance.
The Cultural Impact of Pyramids in Egypt
The pyramids served not only as tombs but also as cultural symbols that represented the might and permanence of the pharaohs. They facilitated the transition of the rulers from the earthly realm to the afterlife, emphasizing the ancient Egyptians’ beliefs in immortality. Festivals, rituals, and pilgrimages often surrounded these structures, underlining their role within the spiritual and daily lives of Egyptians. Furthermore, their grandeur aided in the consolidation of royalty’s divine status, reinforcing pharaonic power over the people.
Understanding Pyramid Construction Techniques
The construction of pyramids involved a complex interplay of technology, labor, and resources, representing an unparalleled achievement in ancient engineering. Various techniques enabled craftsmen to transport and assemble massive stone blocks, while coordinated labor ensured that projects remained on schedule.
Materials Used and Engineering Practices
The primary materials used in pyramid construction included limestone, granite, and basalt, sourced from nearby quarries. The construction techniques involved precise measurements and a sophisticated understanding of geometry. Workers utilized sledges and lubricated logs to transport stones, minimizing friction during movement. These practices exhibited ingenuity in problem-solving, allowing large stones to be moved efficiently over great distances.
Labor Force Involved in Building Pyramids
The labor force for pyramid construction was massive, often numbering in the tens of thousands. Contrary to popular belief, these workers were not slaves; they were skilled laborers who received food and lodging in return for their work. Evidence suggests that workers lived in nearby temporary cities, with organized teams responsible for specific tasks, whether quarrying stone or performing intricate carving. This systematic organization and cooperative labor reflect the advanced societal structure of ancient Egypt.
Architectural Styles Over Eons
The architectural designs of pyramids evolved over the centuries, transitioning from the step pyramids of the Third Dynasty to the smooth-sided true pyramids of the Fourth Dynasty. Each phase signifies technical advancement and responses to the changing socio-religious dynamics of ancient Egypt. As rulers sought to embody divine perfection, their pyramids became progressively grander and more complex, showcasing a growing mastery of architecture.
The Myths and Mysteries Behind the Pyramids
The Pyramids of Giza are enveloped in myths and mysteries, many of which persist to modern day. While historians have uncovered significant information through research and excavations, various unanswered questions continue to intrigue scholars and the public alike.
Common Misconceptions Debunked
Contrary to popular belief, many of the pyramids were not built solely by slaves; instead, they were the work of skilled laborers who were well-fed and organized. Additionally, the idea that aliens built the pyramids has been debunked by researchers who cite evidence of human ingenuity and local labor. Such misconceptions often detract from the incredible accomplishments of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Modern Discoveries and Surprises
Recent archaeological findings, including hidden chambers and previously undiscovered constructions, have shed new light on pyramid construction and usage. Technologies such as ground-penetrating radar have allowed researchers to explore the interiors of these structures without invasive methods, revealing astonishing surprises that challenge long-held theories about their purpose and construction methods.
Ongoing Research and Future Excavations
Ongoing research continues to unlock secrets of the pyramids, with many excavation projects taking place at and around the Giza Plateau. Studies focus on the workforce, construction techniques, and the socioeconomic implications of pyramid building. These insights not only clarify the methods used but also offer perspectives on how such monumental tasks shaped ancient Egyptian society and culture at large.
Tourism and Preservation of the Pyramids
The Pyramids of Giza attract millions of tourists each year, making them some of the most visited cultural sites in the world. While tourism provides economic benefits, it poses challenges to the preservation of these ancient structures. Balancing tourism with conservation is essential for maintaining the integrity of these archaeological wonders.
Current Tourism Trends at the Pyramids
In recent years, tourism rates have surged, with visitors eager to witness the marvels of ancient engineering firsthand. Guided tours have evolved to include interactive experiences, such as virtual reality applications that immerse tourists in the historical context. However, this increase in foot traffic raises concerns about the potential degradation of the site.
Conservation Efforts to Protect the Site
Conservation efforts are pivotal in safeguarding the pyramids from environmental and human-induced damage. Initiatives include limiting access to specific areas, employing advanced technology for restoration, and implementing protective measures to manage the impact of tourism. Collaborative efforts between local authorities and international organizations aim to preserve the pyramids for generations to come.
Visitor Experience and Cultural Sensitivity
Enhancing the visitor experience while respecting the cultural significance of the pyramids is critical. Educational programs that emphasize the historical, architectural, and cultural importance of these monuments can foster greater appreciation among tourists. Cultural sensitivity training for guides and staff helps ensure that visitors understand the importance of preserving the site and the legacy of ancient Egypt.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pyramids
What materials were used to construct the pyramids?
The primary materials used included limestone, granite, and basalt. These stones were sourced from local quarries and transported to the construction site, showcasing sophisticated engineering techniques.
How long did it take to build the Great Pyramid?
The Great Pyramid was built over approximately 20 years, employing a large workforce organized systematically to complete the monumental task within this time frame.
Are there any hidden chambers in the pyramids?
Recent discoveries suggest there are hidden chambers yet to be explored fully. Ongoing excavation and ground-penetrating radar studies are revealing new findings regarding the interiors.
What is the purpose of tombs in Egyptian pyramids?
Tombs were constructed to serve as final resting places for pharaohs and high-ranking individuals, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ beliefs about the afterlife and the journey to immortality.
Can visitors access all areas of the pyramids?
Access to the pyramids is regulated to protect their integrity. While some sections may be open to tourists, many areas are restricted for conservation purposes.